Describe the Structure of Prokaryotic Cell
The plasma membrane separates the cell from the outside environment. Eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells.
4 1 Unique Characteristics Of Prokaryotic Cells Biology Libretexts
In addition it may have genetic material called the plasmids.

. Cellulose hemicellulose proteins and pectin in plants. It is absent in Eukaryotic cells of animals. Most importantly all eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus which stores the genetic or hereditary information of that cell.
Create a Venn diagram or concept map that clearly distinguishes bacterial archaeal and eukaryotic cells in terms of their genome organization organelles cell envelopes ribosome size and component molecules and cytoskeleton. The word prokaryote comes from the Greek πρό pro before and κάρυον karyon nut or kernelProkaryotes can be divided into two domains archaea and bacteria. Organisms with this cell type are called prokaryotic organisms or prokaryotes.
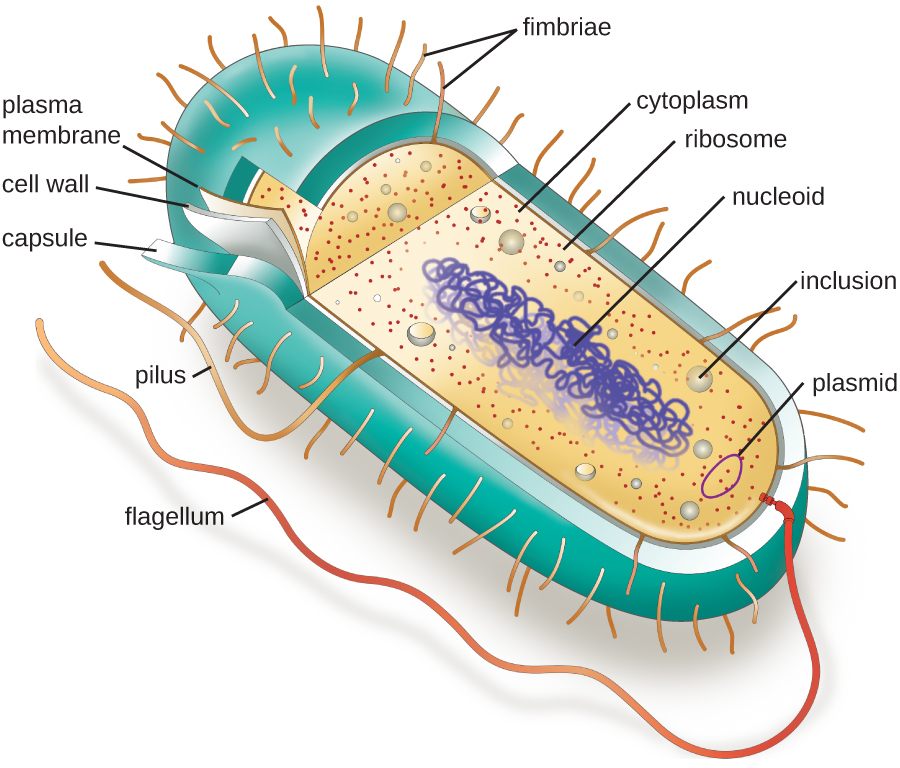
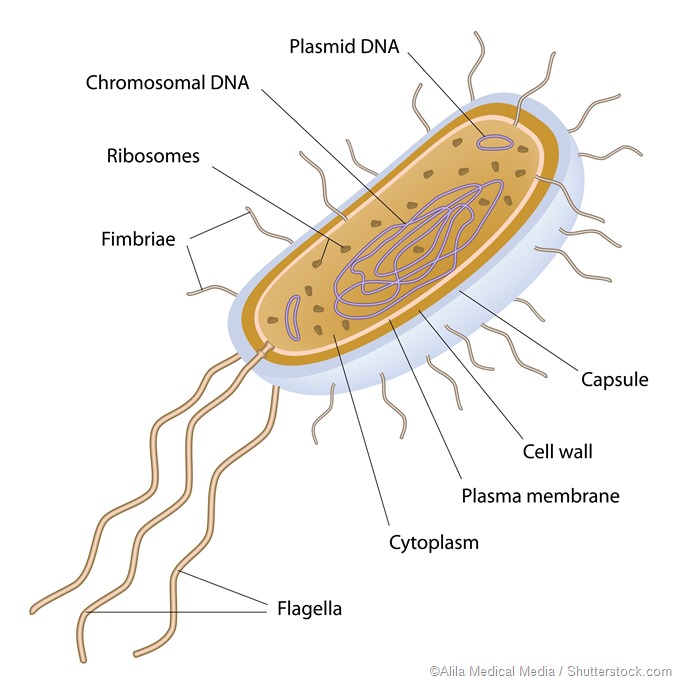
Visible with electron microscope or by staining with Feulgen stain that reacts with DNA D. This imparts the specific shape to the cell and also protects the cell from various environmental conditions. Cell wall Cell membrane Capsule Pili Flagella Ribosomes Plasmids.
Term used to describe aggregated DNA in prokaryote cell B. FUNDAMENTALS OF BIOCHEMISTRY CELL BIOLOGY AND BIOPHYSICS Vol. Explain the difference between bacterial and archaeal cell walls.
The cytoskeleton is. The structure of an animal cell is shown below. Each prokaryotic cell is essentially a one envelop system that consists of protoplasm encased within cell envelope.
They are circular or double-stranded DNA structures. It contains cytoplasm a single primary dsDNA that controls all the activity of the cell. The cell wall is a non-living rigid structure outside the plasma membrane in plant cells and fungi.
Bacteria sometimes occur in groups rather than singly. Like eukaryotic cells prokaryotic cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane and have DNA cytoplasm and ribosomes. It is however absent in animal cells.
- pairs diplococci - chains streptococci - packets sarcinae - clusters staphylococci. Both prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells have ribosomes which are organelles that produce proteins and vacuoles small spaces in cells that store nutrients and help eliminate waste. Bacilli divide along a single axis seen in pairs or chains.
Always double stranded DNA 2. The structures of general eukaryotic and non-photosynthetic prokaryotic cells are diverse. The ultrastructure of a prokaryotic cell particularly a typical bacterial cell consists of cell envelope cytoplasm nucleoid plasmids and surface appendage.
It is made of different components in different Eukaryotes. One single structure is called a pilus and the short form of it is known as fimbriae. Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms and they lack some organelles or other structures like the nucleus.
And eukaryotic cells 1. Like plant cells they also have cell walls. Determine the type of microbe when given a description of a newly discovered microbe.
Haploid normally 1 copy per cell 4. Prokaryotic cells are smaller and do not have membrane-bound nucleus or membrane- bound organelles but do have. A piece of circular double-stranded DNA located in.
The prokaryotic cell structure is composed of. Certain Spirochaeta may be as long as 250 µm although they. Like eukaryotic cells prokaryotic cells have cytoplasm a gel-like substance that makes up the filling of the cell and a cytoskeleton that holds components of the cell in place.
You can refer to the following image for understanding the cell structure. Eukaryotic cells are present in complex living organisms like animals humans and plants. Genetic material of prokaryotes 1.
A cell wall is a rigid structure present outside the plant cell. Attached to cell membranes C. Prokaryotic cells are less complex and much smaller in comparison to eukaryotic cells as they are bacterial cells.
Recall that prokaryotes are unicellular organisms that lack membrane-bound. Ribosomes are only visible with the electron microscope. These are long whip-like protruding structures that help in the locomotion of the cell.
Describe the structure of a prokaryotic cell. Describe the structures that are characteristic of a prokaryote cell. They formed as a result of evolutionary changes that took lace in the prokaryotic cells.
The structures that form the outside of a prokaryotic cell are the capsule the cell wall and the cell membrane. Structure Of Eukaryotic Cell Plasma Membrane. The Prokaryotic Cell Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms that lack organelles or other internal membrane-bound structures.
Prokaryotic cells are single-celled organisms with the deficiency of nucleus and comprise of a capsule cytoplasm cell wall cell membrane ribosome nucleoid plasmids pili and flagella. Plasma membrane cytosol and cytoplasm and ribosomes. Therefore they do not have a nucleus but instead generally have a single chromosome.
Mitochondria are visible with the light microscope but cant be seen in detail. It comprises specific embedded. A prokaryotic cell is a unicellular organism that lacks a membrane-bound nucleus karyon mitochondria or any other membrane-bound organelle.
Prokaryotes contain much less DNA than eukaryotes and have circular chromosomes. A prokaryotic cell consists of a cell envelope made of the cell wall and the cell membrane. Coccidivide on one or more planes producing cells in.
Unlike eukaryotic cells they may have a cell capsule and they have a single large chromosome that is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane. The cell wall in this kind of cell is responsible for the shape of the organism and also serves as their protection. A Two main forms of cells exist.
11 rows The Prokaryotic Cell. These structures are also known as appendages. As previously discussed prokaryotic cells lack an organized nucleus while eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound nuclei and organelles that house the cells DNA and direct the synthesis of ribosomes and proteins.
II - Prokaryotic Cell Structure and Function - T. The nucleus stores chromatin DNA plus proteins in a gel-like substance called the nucleoplasm. Plasmids are the genetic material of a prokaryotic cell.
Downing Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems EOLSS Prokaryotic cells typically range in size from 02 µm to 20 µm in diameter and from 1 to over 6 µm in length.

Prokaryotic Cell Structure Characteristics Function
Comments
Post a Comment